 |
 |
- Search
| Obstet Gynecol Sci > Volume 60(5); 2017 > Article |
Abstract
Metastasis to the female genital tract from extragenital primary cancer is uncommon. In this case, a 46-year-old woman was diagnosed with invasive lobular carcinoma of the left breast in 2011. She had left breast conserving surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, and hormonal therapy (gosereline and tamoxifen). However, she developed menorrhagia after interruption of hormonal therapy and incidentally, the ultrasonogram of her pelvis showed a solid, large mass in the cervix. It looked like leiomyoma. Because of massive vaginal bleeding requiring multiple blood transfusions, she underwent total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. Unexpectedly, however, histopathological examination revealed metastatic carcinoma, consistent with breast origin.The metastatic tumor involved the uterine corpus with spreading to the endocervix, left ovary, and multiple lymphovascular invasion was present. We described the rarity and risk of metastatic uterine cancer in patient with history of malignant tumor treatment.
Metastasis to the female genital tract from extragenital primary cancer is uncommon. However, the breast and intestine are the most common primary sites in patients with metastatic genital tract tumor. The ovary and vagina are common organs of breast cancer metastases in the genital tract. Yet, metastases to the cervix uteri are extremely rare, with an estimated incidence of 0.8-1.7% [1,2]. Here, we describe a patient in whom metastatic breast cancer of the cervix appeared as a large cervical leiomyoma and was diagnosed after treating of the primary tumor.
A 46-year-old woman (gravida 2, para 2) was diagnosed as having invasive lobular carcinoma of the left breast in 2011. Clinical and ultrasonographic examinations and a mammogram showed a category 6, highly suspicious tumor of 4 cm in the left breast. The gross appearance of the mass was 2 bodies of brownish white soft tissue, measuring 2 cm long. She underwent a needle biopsy at the 6 o'clock position of the left breast. The biopsy result was invasive lobular carcinoma. She did not have evidence of metastasis on positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) and pelvic magnetic resonance imaging scans. She underwent 2 cycles of neoadjuvant chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide (Baxter Healthcare Corporation, Deerfield, IL, USA) and adriamycin (Pfizer Inc., New York, NY, USA). The breast mass decreased from 4 to 2cm. Subsequently, left breast conserving surgery was performed with dissection of axillary lymph nodes was made. The initial tumor, node, and metastasis stage was pT1, N0, M0; the estrogen and progesterone receptors were positive; and the expression of C-erb-B2-coding, K-ras oncogene was positive. However, epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin) was negative. An additional 4 cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy with cyclophosphamide and adriamycin, and total dose 50.4 Gy (6 weeks/28 fractions) of radiation therapy were administered. She also took hormone therapy (goserelin and tamoxifen; AstraZeneca Pharmaceuticals LP, Wilmington, DE, USA) for 2 years. At that time, she was also checked by gynecologist. The gynecological examination and ultrasonography showed a tumor (3.5 cm) of the cervix, but further details were unavailable (Fig. 1A and B). Exfoliative cytology (Papanicolaou smear) results were negative. We considered that the cervical mass was a simple leiomyoma because of no evidence of metastasis on the PET-CT scan. Therefore, she underwent regular follow-up at the breast clinic without any evidence of recurrence.
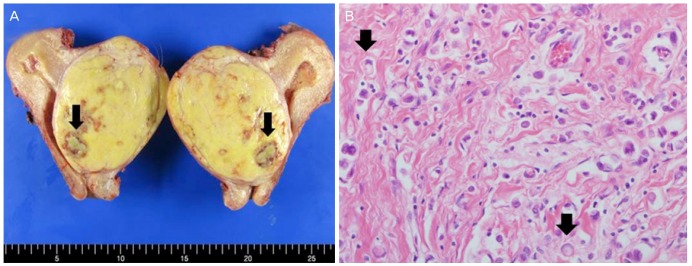
Twenty-four months after treatment, she visited the hemato-oncologic department for persistent anemia, and she was diagnosed as having severe myelofibrotic marrow based on a bone marrow examination. Menorrhagia also made the anemia, so she stopped the tamoxifen therapy. Incidentally, the ultrasonography of her pelvis showed a solid, large mass in the cervix measuring more than 8 cm in diameter and appearing as a submucosal leiomyoma on the isthmic portion.The serum cancer antigen 125 (CA125), CA15-3, carcinoembryonic antigen, and estradiol (E2) levels were 535.4 U/mL, 5.0 U/mL, 1.8 U/mL, and 39.3 pg/mL, respectively. The mass of the cervix was larger than before, and she had more profuse vaginal bleeding requiring multiple blood transfusions. She underwent total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy. The removed uterus weighed 484 g. The cervix was fish-mouthed shaped. The cervical mass (9.5×7.5 cm) was not encapsulated. The cut surface of the mass was yellowish gray, solid, and necrotic. Both the salpinx and ovaries were not specific on gross findings (Fig. 2A). Unexpectedly, the histopathological examination showed metastatic carcinoma consistent with an origin of the breast (Fig. 2B). The metastatic tumor involved the uterine corpus and spread to the endocervix and left ovary, and multiple lymphovascular invasions were present. Otherwise, the right ovary and both salpinges were normal. Immunohistochemical staining of the tumor was positive for the estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, cytokeratin,and gross cystic disease fluid protein-15. She was discharged home 8 days postoperatively. She will be evaluated by PET-CT, bone scan, and breast sonography, tumor markers will be assessed, and the next second-line chemotherapy will be planned.
In the present case, pathological results after total hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy showed metastatic carcinoma consistent with primary breast cancer. This is the first case report of breast cancer metastasis occurring as a disseminated disease with isolated involvement of the cervix in Korea.
Metastatic disease from the breast to the female genital tract most often involves the ovaries. Metastasis of breast cancer to the uterus has been described in more than 200 patients [3]. The cervix is a small organ comprised predominantly of fibromuscular tissue with a limited blood supply and only afferent lymphatic drainage, making it a less favorable site for metastasis [4]. Approximately 30 patients with breast cancer metastases to the uterine cervix have been previously reported [2,5]. Most cases of breast cancer with genital tract metastasis occurred in patients with advanced breast cancer while on tamoxifen treatment or during follow-up. In 67%-89% of the reported cases, distant metastases of other sites were present at diagnosis of cervical metastasis [5]. In our case, breast cancer was found in the early stage and has undergone complete treatment of breast cancer. She was attended regular follow-up visits without recurrence. This highlights the rarity of presentation in our patient.
It is easy to mistake the common presentation of abnormal vaginal bleeding as primary disease rather than metastatic involvement of the genital tract. Vaginal bleeding should be differential diagnosis cervical myoma, uterine metastasis, endometrial lesion especially in women with a history of breast cancer. Because patient with breast cancer took a tamoxifen which increases primary endometrial carcinoma, endometrial proliferation, and endometrial hyperplasia [6]. We thought that the patient had cervical leiomyoma at the time of the diagnosis and an enlarged cervical mass after finishing treatment. Preoperatively it is impossible to distinguish metastatic growth from hormone-sensitive growth induced by tamoxifen.
Breast cancer includes numerous histological subtypes, of which the 2 most common are infiltrating duct carcinoma and infiltrating lobular carcinoma [4]. Our patient was diagnosed as having infiltrating lobular carcinoma. The lobular histopathologic type seems to metastasis to the genital tract more frequently than ductal tumors [4]. Additionally, unlike invasive ductal carcinoma, lobular carcinoma exhibits a distinct metastatic pattern. Distant lobular carcinoma tends to diffusely infiltrate organs, and it surfaces in the bones, gastrointestinal tract, peritoneum, and retroperitoneum, including the uterine myometrium, endometrium, and cervix as well as ovaries, ureters, and stomach, especially if hormone receptors are positive [4,7,8]. The exact mechanism for this unusual metastatic pattern is unknown. The loss of E-cadherin expression on a tumor cell membrane is a characteristic feature of lobular carcinoma. The loss of E-cadherin expression is associated with abnormalities in catenin expression, which leads to a loss of cell-to-cell adhesion and intracellular and intercellular signaling. This is postulated as the mechanism for the unusual metastatic pattern of lobular carcinoma [4].
The time between the initial diagnosis of breast carcinoma and the development of uterine cervical metastasis differed in our patient (5 years after the initial diagnosis), emphasizing the importance of regular gynecological examinations in this patient.
References
1. Kamby C, Vejborg I, Kristensen B, Olsen LO, Mouridsen HT. Metastatic pattern in recurrent breast cancer. Special reference to intrathoracic recurrences. Cancer 1988;62:2226-2233. PMID: 3179937.


2. Pomerance W, MacKles A. Adenocarcinoma of the cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1962;84:367-374. PMID: 14487719.


3. Green AE, Biscotti C, Michener C, Belinson J. Isolated cervical metastasis of breast cancer: a case report and review of the literature. Gynecol Oncol 2004;95:267-269. PMID: 15385145.


4. Lokadasan R, Ratheesan K, Sukumaran R, Nair SP. Metastatic lobular carcinoma of breast mimics primary cervix carcinoma: two case reports and a review of the literature. Ecancermedicalscience 2015;9:571PMID: 26435744.



5. Abell MR, Gosling JR. Gland cell carcinoma (adenocarcinoma) of the uterine cervix. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1962;83:729-755. PMID: 13858921.


6. Piura B, Yanai-Inbar I, Rabinovich A, Zalmanov S, Goldstein J. Abnormal uterine bleeding as a presenting sign of metastases to the uterine corpus, cervix and vagina in a breast cancer patient on tamoxifen therapy. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1999;83:57-61. PMID: 10221611.


7. Pestalozzi BC, Zahrieh D, Mallon E, Gusterson BA, Price KN, Gelber RD, et al. Distinct clinical and prognostic features of infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast: combined results of 15 International Breast Cancer Study Group clinical trials. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:3006-3014. PMID: 18458044.


8. Sastre-Garau X, Jouve M, Asselain B, Vincent-Salomon A, Beuzeboc P, Dorval T, et al. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast. Clinicopathologic analysis of 975 cases with reference to data on conservative therapy and metastatic patterns. Cancer 1996;77:113-120. PMID: 8630916.


Fig. 1
(A) Vaginal ultrasonography showing a tumor of the cervix (uteri, 3.4 cm in diameter). (B) The cervix appears as a large, cervical leiomyoma (8.7 cm in 2017).
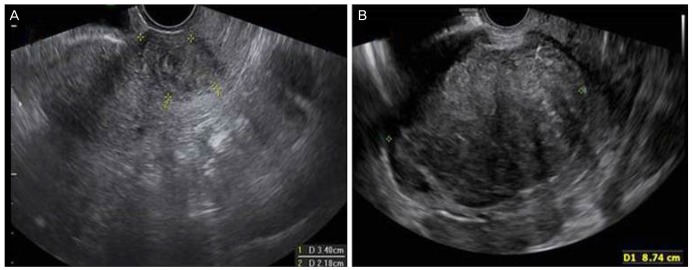
Fig. 2
(A) The cut surface of the bisected uterus in the direction from anterior to posterior shows a well demarcated, solid, mass-like lesion; the lesion is yellow, it contains necrotic focus (arrow). (B) Tumor cells lack cohesion and appear individually dispersed through a collagenous stroma, and they occasionally have a signet-ring cell appearance with intracytoplasmic mucin.
-
METRICS

- Related articles in Obstet Gynecol Sci
-
Metastatic malignant melanoma with peritoneal seeding in a young woman: A case report2014 May;57(3)




















